|
Strain Name
|
CB17/lcr-PrkdcscidNcr1tm1(NCR1)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name
|
B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID)
|
|
Background
|
CB-17 SCID
|
Catalog number
|
112259
|
|
Aliases
|
CD335, LY94, NK-p46, NKP46
|
Protein expression analysis
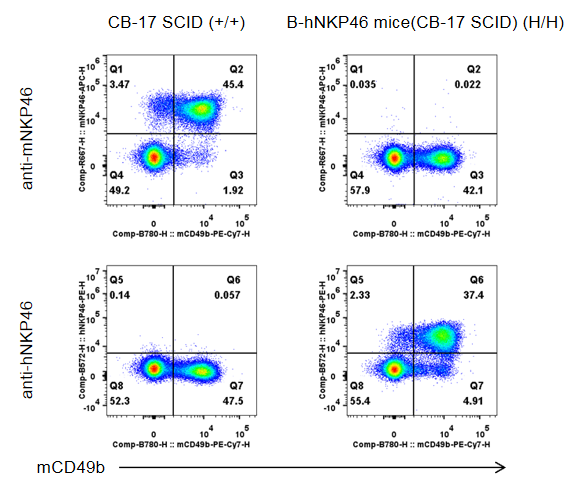
Strain specific NKP46 expression analysis in wild-type and B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from CB-17 SCID (+/+) and homozygous B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (H/H), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific NKP46 antibody. Mouse NKP46 was detectable in wild-type mice. Human NKP46 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID).
Protein expression of NKP46 in spleen
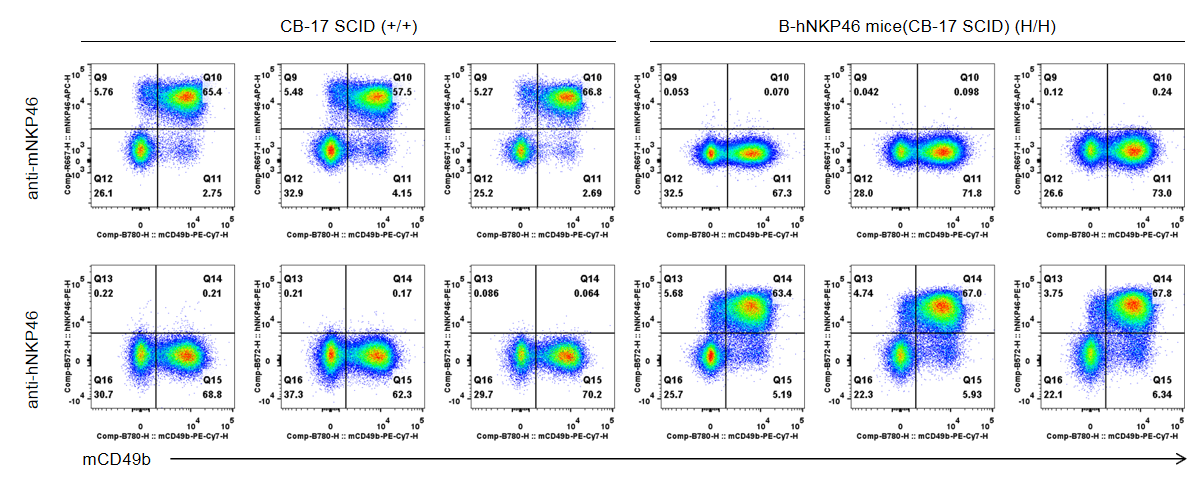
Strain specific NKP46 expression analysis in wild-type and B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from CB-17 SCID(+/+) and homozygous B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID)(H/H) (n=3, 6-week old), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific NKP46 antibody. Mouse NKP46 was detectable in wild-type mice. Human NKP46 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID).
Protein expression of NKP46 in bone marrow
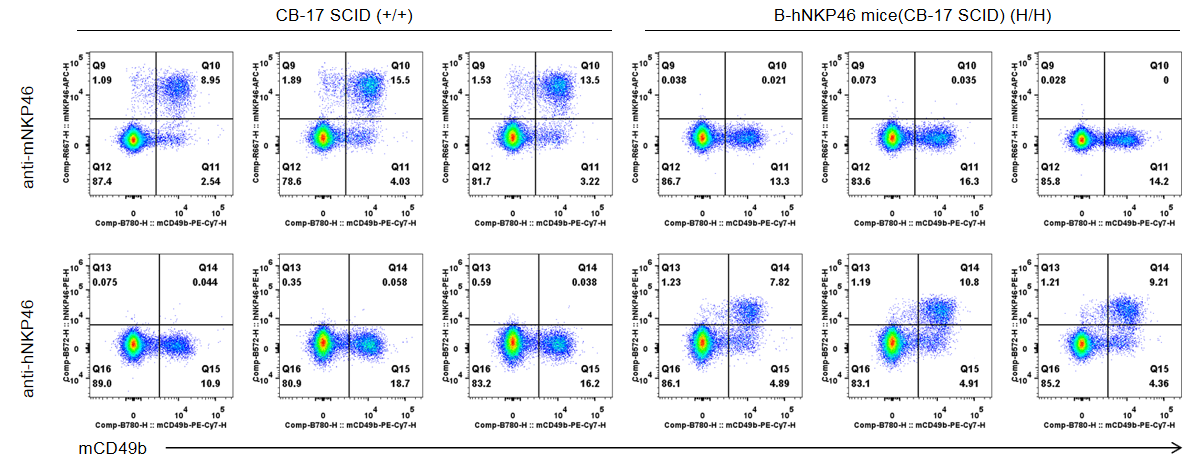
Strain specific NKP46 expression analysis in wild-type and B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) by flow cytometry. Bone marrow were collected from CB-17 SCID(+/+) and homozygous B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID)(H/H) (n=3, 6-week old), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific NKP46 antibody. Mouse NKP46 was detectable in wild-type mice. Human NKP46 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID).
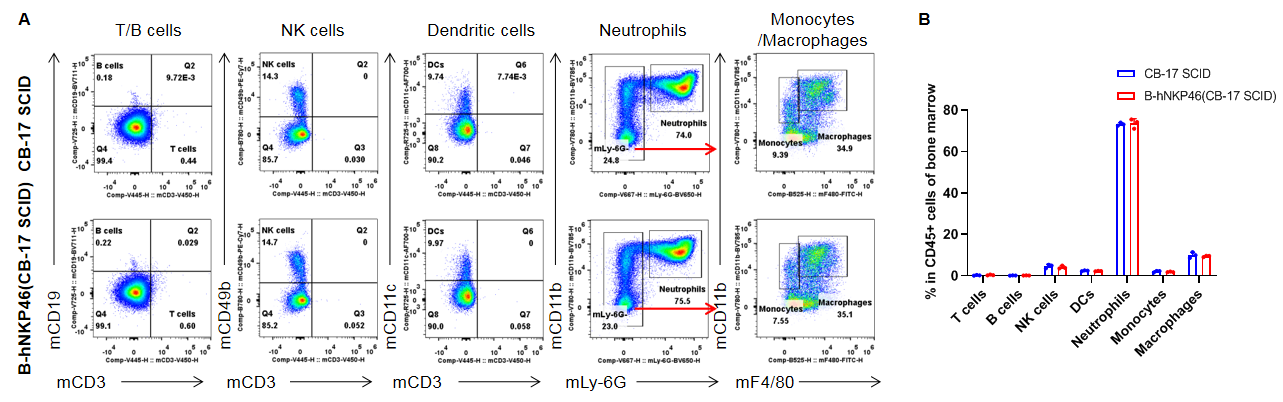
Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in spleen

Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Splenocytes were isolated from female CB-17 SCID and B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, granulocytes, monocytes and macrophages in homozygous B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) were similar to those in the CB-17 SCID mice, demonstrating that NKP46 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in bone marrow
Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Bone marrow cells were isolated from female CB-17 SCID and B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, granulocytes, monocytes and macrophages in homozygous B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) were similar to those in the CB-17 SCID mice, demonstrating that NKP46 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in bone marrow. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in blood
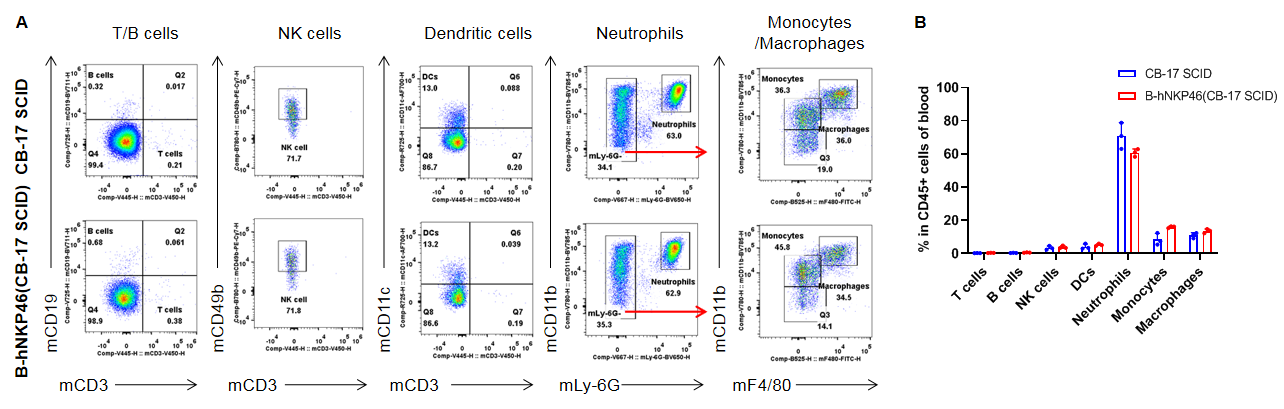
Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Blood cells were isolated from female CB-17 SCID and B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, granulocytes, monocytes and macrophages in homozygous B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) were similar to those in the CB-17 SCID mice, demonstrating that NKP46 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in blood. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
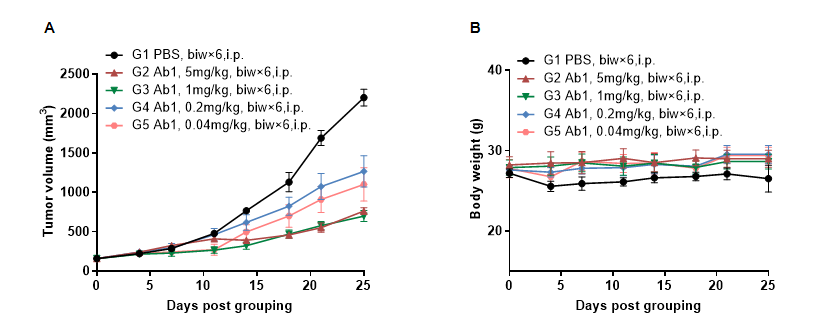
In vivo efficacy of anti-human NKP46-based Ab in B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID)
Antitumor activity of anti-human NKP46-based Ab in B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID). (A) Anti-human NKP46-based Ab inhibited BxPC-3 tumor growth in B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID). BxPC-3 cells (5E6) were subcutaneously implanted into B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (male, 7-8 week-old, n=4). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 150-200 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human NKP46-based Ab with doses and schedules indicated in panel A. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human NKP46-based Ab was efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. (All antibodies were provided by the clients)
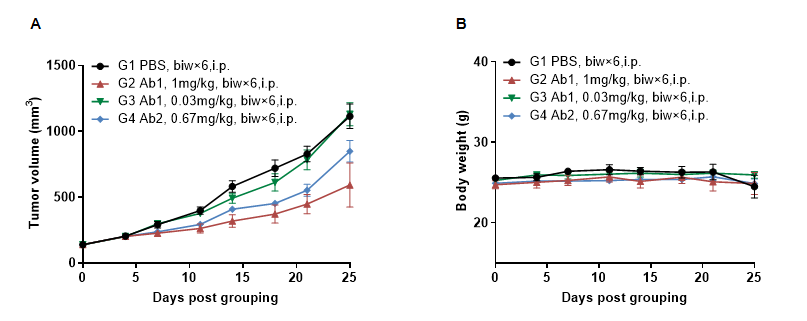
In vivo efficacy of anti-human NKP46-based Ab in B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID)
Antitumor activity of anti-human NKP46-based Ab in B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID). (A) Anti-human NKP46-based Ab inhibited BxPC-3 tumor growth in B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID). BxPC-3 cells (5E6) were subcutaneously implanted into B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID) (male, 7-8 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100-150 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human NKP46-based Ab with doses and schedules indicated in panel A. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human NKP46-based Ab was efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-hNKP46 mice(CB-17 SCID). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. (All antibodies were provided by the clients)